
SEVEN YEAR ITCH SCABIES SKIN
Scabies can spread rapidly under crowded conditions where close body and skin contact is frequent.

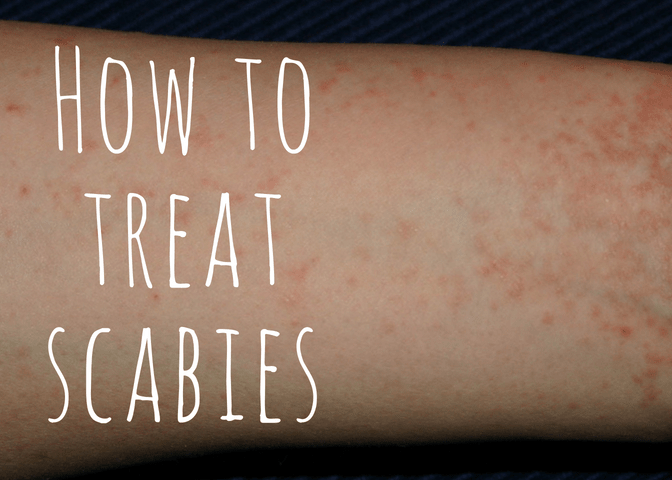
Scabies is found worldwide and affects people of all races and social classes. The scabies mite usually is spread by direct, prolonged, skin-to-skin contact with a person who has scabies. The most common symptoms of scabies are intense itching and a pimple-like skin rash. The microscopic scabies mite burrows into the upper layer of the skin where it lives and lays its eggs. Scabies is an infestation of the skin by the human itch mite ( Sarcoptes scabiei var.
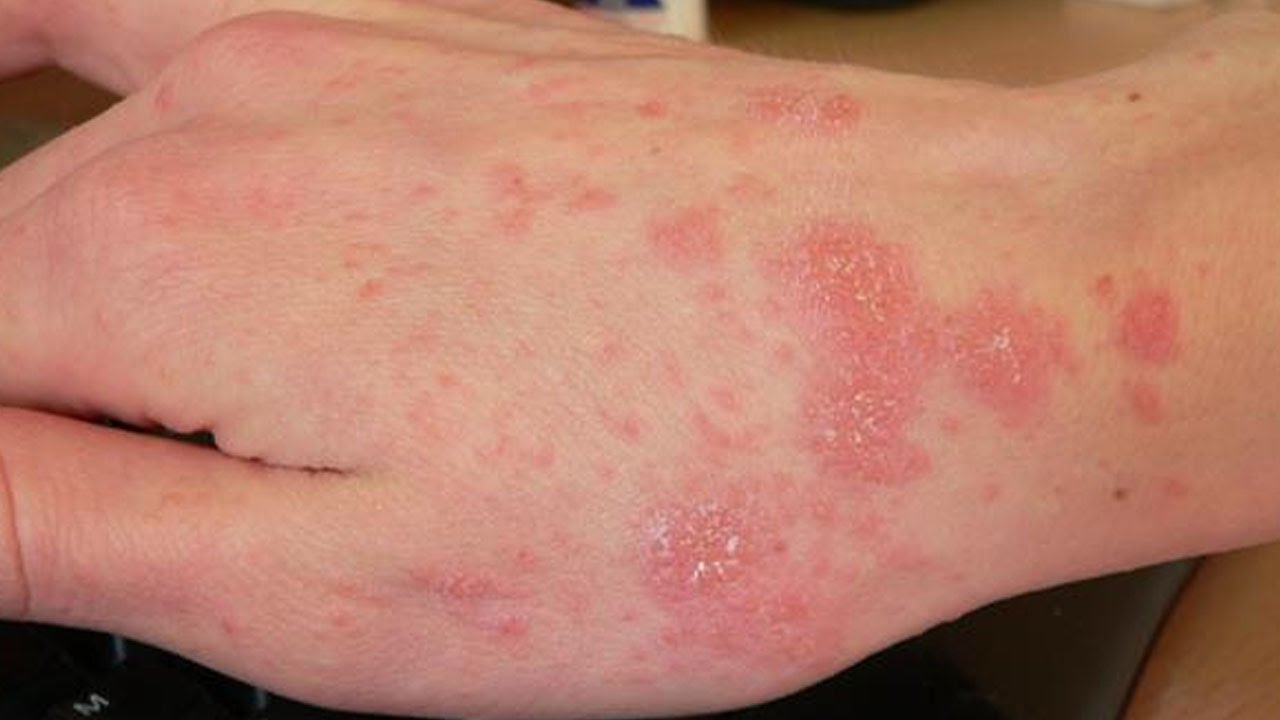
My spouse and I were diagnosed with scabies.How can I remove scabies mites from my clothes?.How can I remove scabies mites from my house or carpet?.Can scabies be spread by swimming in a public pool?.How soon after treatment will I feel better?.What are the signs and symptoms of scabies infestation?.How soon after infestation do symptoms of scabies begin?.You can use tea tree oil, borax, Lysol, hydrogen peroxide, and lemon/olive oil to clean your beddings and carpets. Vacuum all carpets and rugs or wash them with hot water as well. By inhibiting them from escaping, you will kill the little buggers. Mites that cause scabies could survive away from human skin for several days. For clothing and items that are not machine washable, seal them all in a plastic container for at least a week. Use hot water when cleaning your beddings and clothing to kill all mites. Preventing Further InfestationĪpart from getting the right medication to treat scabies, remove all beddings, clothes, and any other articles of clothing you used in the last three days and have it cleaned. This will ease the itchiness so you don’t aggravate the condition of your skin. If you have open sores and you cannot stop yourself from scratching, take anti-histamine medications. These mites usually lay eggs underneath the nails to protect them from the elements. In addition, cut all your nails to remove mite eggs. Still, it’s important to get medical help right away so you don’t spread the infestation to your loved ones. In some cases, patients do not suspect scabies because the symptom that manifest is rashes, rather than itching. If you suspect that you have scabies, it’s best to have yourself checked for a diagnosis. Scabies should be treated with medication. Scaly skin and skin rashes will also develop on the affected area. Scabies also affect the fingers, toes, buttocks, waist, and any crevices of the body. Upon close inspection of the skin, you will find something burrowed underneath, indicating that the mites are on the move under your skin. Continuous scratching will lead to sores. The bites are concentrated on the knees or underarm, elbows, or wrists.
30469-3.jpg)
Bites from the mites will look like common insect bites. One of the major tell-tale signs of scabies is itchy lesions on the skin. Human-to-animal transmission of scabies is unlikely. When mites are away from human skin, they will only live for two to three days. But this isn’t the majority of the transmission of scabies. Sleeping on the same bed as well as sharing clothes with a person afflicted with scabies will also cause infestation. However, scabies is not classified as a sexually transmitted disease it’s just contagious. During sexual intercourse, scabies could cause skin lesions on the groin area, the penis, and vagina. But as the condition progresses, it will start spreading to other parts of the body as well. Usually, symptoms of scabies will manifest on the affected area. Therefore, it’s spread through skin contact. The mites that cause this condition could be passed from one person to another. In animals, the mites that cause mange is different but related specie. This type of mite could infect both humans and animals alike. Sarcoptes scabiei is a small parasite that burrows into the host’s skin, causing intense itching and triggering an allergic response. Scabies, also known colloquially as the “seven year itch,” refers to a highly contagious skin infection caused by Sarcoptes scabiei, a specie of mites.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
